Blogs
How to leverage different state management techniques with Flutter for a seamless user experience

 When building mobile or web applications, managing the state, which represents the data and its behavior within the app, becomes a critical aspect of the development process. State management in Flutter refers to the process of managing and updating the state of the application to ensure smooth user interactions and consistent data flow.
When building mobile or web applications, managing the state, which represents the data and its behavior within the app, becomes a critical aspect of the development process. State management in Flutter refers to the process of managing and updating the state of the application to ensure smooth user interactions and consistent data flow.
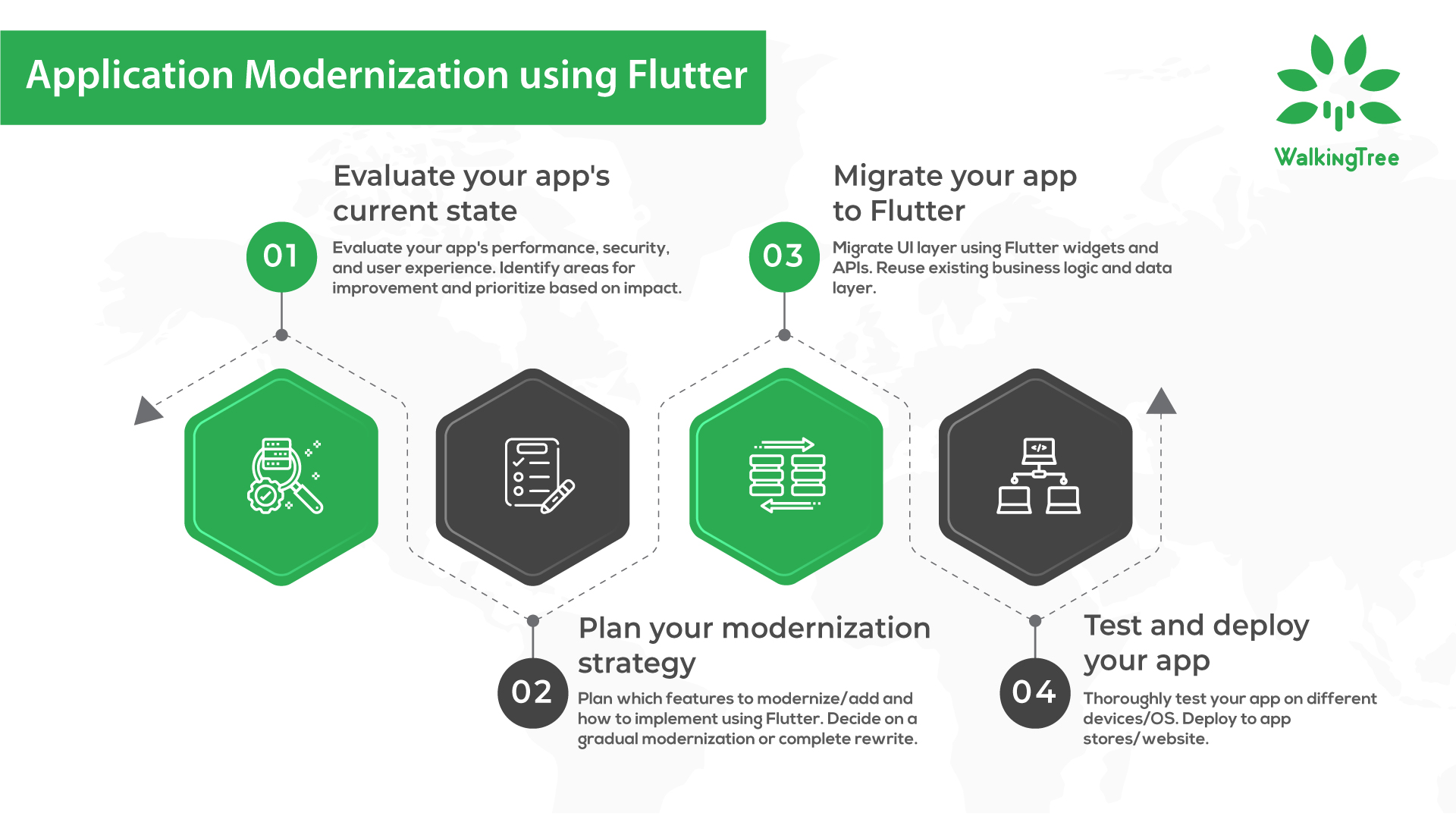
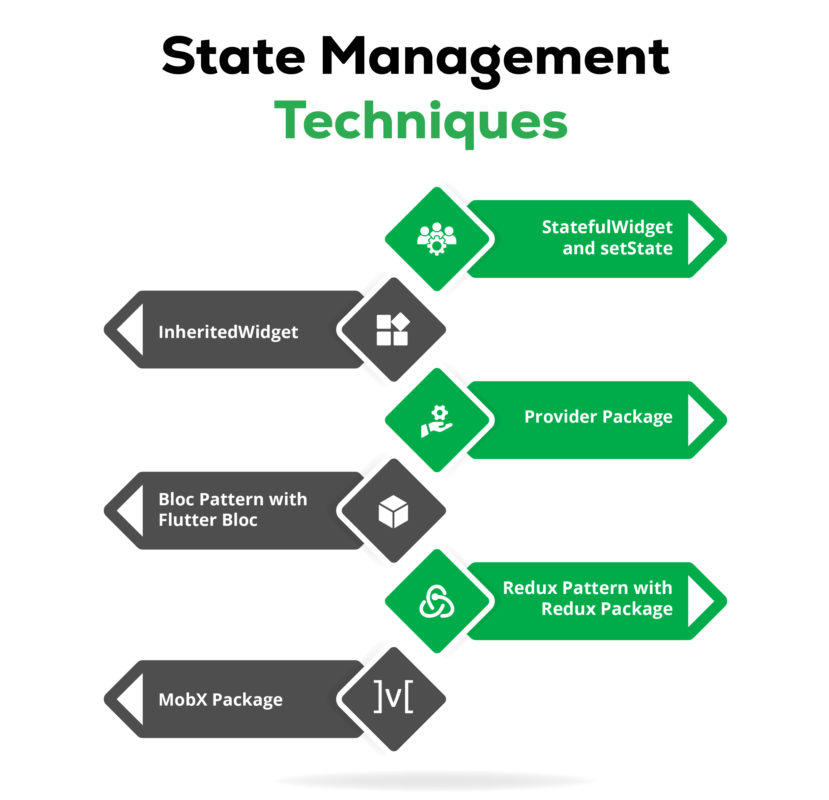
In this blog, we will explore different state management approaches in Flutter and provide examples to illustrate each method. We will cover the following state management techniques:
- StatefulWidget and setState
- InheritedWidget
- Provider Package
- Bloc Pattern with Flutter Bloc
- Redux Pattern with Redux Package
- MobX Package
StatefulWidget and setState:
StatefulWidget is one of the simplest forms of state management in Flutter. It involves creating a widget that holds mutable state data using a StatefulWidget class. The widget’s state can be updated using the setState method, which triggers a rebuild of the widget and its child subtree.
Example:
dart
Copy code
class CounterWidget extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_CounterWidgetState createState() => _CounterWidgetState();
}
class _CounterWidgetState extends State<CounterWidget> {
int _counter = 0;
void _incrementCounter() {
setState(() {
_counter++;
});
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Column(
children: [
Text('Counter: $_counter'),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: _incrementCounter,
child: Text('Increment'),
),
],
);
}
}
InheritedWidget
InheritedWidget is a widget that allows data to be passed down the widget tree efficiently and conveniently. It is often used when you have data that needs to be accessible to many widgets in the tree without explicitly passing it through each constructor.
Example:
dart
Copy code
class DataContainer extends InheritedWidget {
final int data;
DataContainer({required this.data, required Widget child})
: super(child: child);
static DataContainer? of(BuildContext context) {
return context.dependOnInheritedWidgetOfExactType<DataContainer>();
}
@override
bool updateShouldNotify(DataContainer oldWidget) {
return data != oldWidget.data;
}
}
// Usage
class MyWidget extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final dataContainer = DataContainer.of(context);
int data = dataContainer?.data ?? 0;
return Text('Data from InheritedWidget: $data');
}
}
Provider Package
The Provider package is a popular state management solution in Flutter that simplifies the process of managing and accessing state throughout the widget tree. It is based on Inherited Widgets but provides a more convenient and readable syntax.
Example:
dart
Copy code
class CounterProvider extends ChangeNotifier {
int _counter = 0;
int get counter => _counter;
void incrementCounter() {
_counter++;
notifyListeners();
}
}
// Usage
class MyWidget extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final counterProvider = Provider.of<CounterProvider>(context);
int counter = counterProvider.counter;
return Column(
children: [
Text('Counter from Provider: $counter'),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () => counterProvider.incrementCounter(),
child: Text('Increment'),
),
],
);
}
}
Bloc Pattern with Flutter Bloc
BLoC (Business Logic Component) is a design pattern that separates business logic from UI. The Flutter Bloc library simplifies the implementation of this pattern.
Example:
dart
Copy code
// Define events
enum CounterEvent { increment }
// Define the BLoC
class CounterBloc extends Bloc<CounterEvent, int> {
CounterBloc() : super(0);
@override
Stream<int> mapEventToState(CounterEvent event) async* {
if (event == CounterEvent.increment) {
yield state + 1;
}
}
}
// Usage
class MyWidget extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
final counterBloc = BlocProvider.of<CounterBloc>(context);
int counter = BlocProvider.watch<CounterBloc>(context).state;
return Column(
children: [
Text('Counter from BLoC: $counter'),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () => counterBloc.add(CounterEvent.increment),
child: Text('Increment'),
),
],
);
}
}
Redux Pattern with Redux Package
Redux is a predictable state management container that helps manage state in large-scale applications. It follows a unidirectional data flow and is based on the principles of Flux.
Example:
dart
Copy code
// Define actions
enum CounterAction { increment }
// Define the reducer
int counterReducer(int state, dynamic action) {
if (action == CounterAction.increment) {
return state + 1;
}
return state;
}
// Create the store
final store = Store<int>(counterReducer, initialState: 0);
// Usage
class MyWidget extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
int counter = store.state;
return Column(
children: [
Text('Counter from Redux: $counter'),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () => store.dispatch(CounterAction.increment),
child: Text('Increment'),
),
],
);
}
}
MobX Package
MobX is a state management library that allows you to create reactive observables, reactions, and actions. It ensures that changes to observables automatically update the relevant parts of your application.
Example:
dart
Copy code
// Define a MobX store
class CounterStore = _CounterStore with _$CounterStore;
abstract class _CounterStore with Store {
@observable
int counter = 0;
@action
void incrementCounter() {
counter++;
}
}
// Usage
class MyWidget extends StatelessWidget {
final CounterStore counterStore = CounterStore();
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Column(
children: [
Observer(
builder: (_) => Text('Counter from MobX: ${counterStore.counter}'),
),
ElevatedButton(
onPressed: () => counterStore.incrementCounter(),
child: Text('Increment'),
),
],
);
}
}
No hard work for state management with Flutter, happy coding!
In this blog post, we explored various state management approaches in Flutter, ranging from simple techniques like StatefulWidget with setState to more advanced libraries like Redux and MobX. Each approach has its strengths and use cases, and the choice of state management depends on the complexity and requirements of the application.
By understanding different state management patterns and their implementations, Flutter developers can efficiently handle application states, leading to more maintainable and scalable code. Happy coding!