Blogs
Actors, Architecture & Transaction flow in Hyperledger fabric
In my previous article, we learned to set up the Hyperledger composer development environment.
In this article, we will focus on the actors who would be part of the Hyperledger blockchain ecosystem, the Hyperledger fabric architecture, and the transaction flow in the fabric which would help us to understand the ground before we build a sample business application.
The Hyperledger composer helps the actors in the network with different tools who would be part of building the business blockchain applications. The actors have individual roles in blockchain development, deployment, and utilization. Following are the actors in the Blockchain solution.
Actors in the Hyperledger fabric Blockchain
Like any application development, we need an Architect, Developer, Network Admin, and an End User who interacts with the application. In the Blockchain, with these primary actors, we also need regulators who act as an Auditor, the Certificate Authorities for issuing certificates for access and the Data Sources for accessing data. Every actor in the blockchain ecosystem has different roles to play which enables the system to have demarcated processes.
Here in this article, I will precisely discuss some of the important actors who plays the major role in the Blockchain ecosystem
Blockchain Architect
An Architect / Business Analyst who uses the composer modeling language to create the business network model. He/She is responsible for the architecture and the design of the blockchain solution.
Blockchain Developer
Who writes the smart contract/business logic which interacts with the Blockchain. In Hyperledger fabric the chain code can be written either in Node or Go.
Blockchain Network Operator
Who manages and monitors the Blockchain network. His/Her functions would vary from deployment to issuing of cards, upgrading to updating the newer versions of BNA files etc.
Hyperledger Fabric Architecture
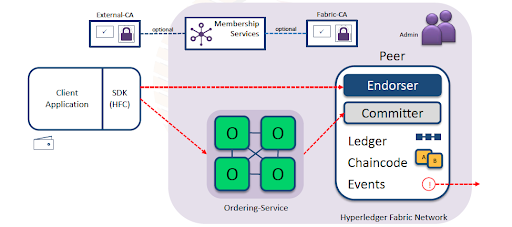
In the fabric architecture, the key components are:
- Membership Services
- Certificate Authorities
- Nodes
- Peers
Membership Services:
The main function of the membership service is to provide the identity to the users who are going to transact in the Blockchain network and it is done simply by digital certificates. Users use this digital certificates to sign the transactions and submit it to the blockchain. The digital certificate issued to the user would have the authentication to get into the system and a certain level of privileges for right access depending upon the roles the user performs.
Certificate Authorities:
The certificate authority in the Hyperledger is pluggable and so it can either be an internal or an external certificate authority. The certificates rely on the Public Key Infrastructure where the Certificate authority would announce in the network that a particular public key is of a particular user and then the user would use his private key to transact.
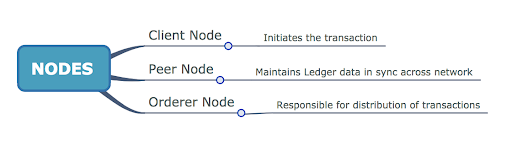
Nodes:
In the permissioned blockchain network, all the nodes are not equal as in the public blockchain network where all nodes are equal. In the public blockchain network, every user is a node and has to download the node software to participate in the blockchain network. Simply, for the public blockchain, the node software is WALLET. Whereas in the permissioned blockchain network we have different nodes like client node, peer node & orderer node and each has different roles to play.
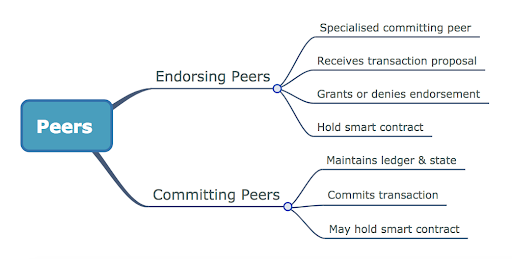
Peers:
Peers are an important component in the Blockchain infrastructure and every organization in the Blockchain would have one or more peers in the network they are connected with. The peers again play different roles like endorsing peers & committing peers and these roles are assigned during the setup of the network.
The orderer node is responsible for the distribution of the data. The main goal of the ordering service is to totally give ordered set of transactions. The ordering service would put the transactions from multiple peers in an order and then sends to each peer as a block to get updated in the ledger.
Transaction Flow
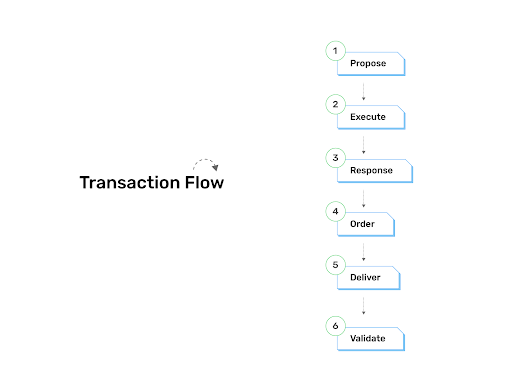
So, whenever a client needs to initiate a transaction in a blockchain network, the client with the application interacts with the blockchain using the Hyperledger Fabric SDK. The authentication and the user privileges are taken care by the membership services and the certificate authority would be assigning a public key and a private key to each user in the network.
The client PROPOSES the transactions to the endorsing peers who in turn would capture the read-write sets and validate with the smart contract available. This endorsement is called EXECUTION. Once the execution is done at the endorsement peer the RESPONSE would be sent back to the client with endorsement signatures. All the responses would be Asynchronous as there would be multiple transactions from multiple peers in the network. The further process of the transaction depends on the endorsement policy which is decided during the initial setup of the network. Suppose the transaction have the required endorsements then it would be forwarded for ORDERING the transaction.
Once the transaction is submitted to the ordering service, the ordering service would order them as ordered set here and then DELIVER to all the peers in the network. The ordered set of transactions are called blocks.
The ordering service in the Hyperledger fabric is also pluggable and the organizations can also use their own ordering service they desire. Some of the ordering services used in the fabric are SOLO, Kafka ordering service (Crash fault tolerance) and presently Byzantine Fault Tolerance (BFT) consensus is being used.
Finally, the transactions sent from the ordering service is VALIDATED at each peer end for sufficient endorsements and also to check the consistency of the transaction. Once the validation is done each of the peers emit events which would tell either the transaction is valid or invalid.
SUMMARY
In this article, we discussed the actors who will be participating in the blockchain network. It is very important to identify and demarcate the actors during the initial setup of the network as the network would involve different organizations who would be part of different blockchain networks separated by different channels and ledgers. We also discussed the architecture of the Hyperledger Fabric network and the main components in it. The fabric is designed in a way where many components can be customized depending upon the network requirements. Finally, we discussed the transaction flow in the network.
At WalkingTree we are excited about the possibilities that Hyperledger technology brings in for the new age Blockchain applications. Hope this article will save a good amount of time for you when you come across this kind of need.
If you want your thoughts or proof of concepts around Blockchain to be validated by the industry experts? We will be excited to guide you!