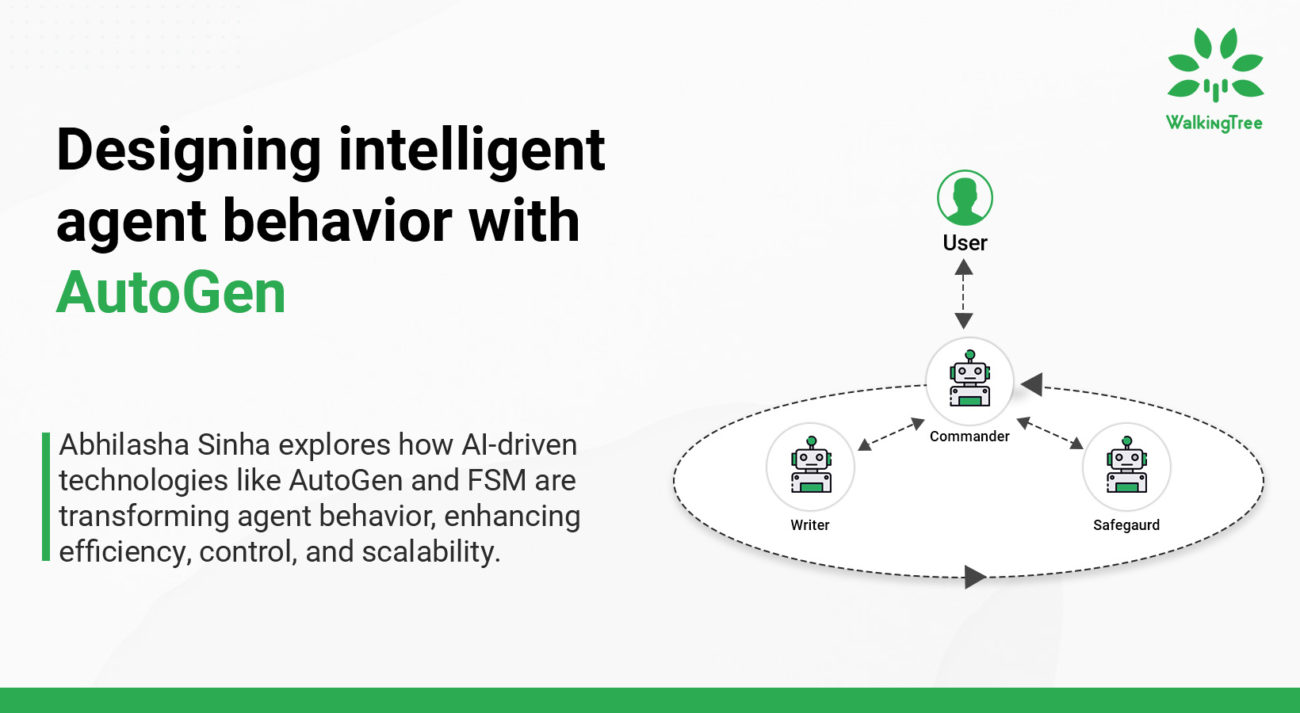
Assuring Quality within Cloud Architectures: Advanced Security Protocols for the Cloud Speed Layer
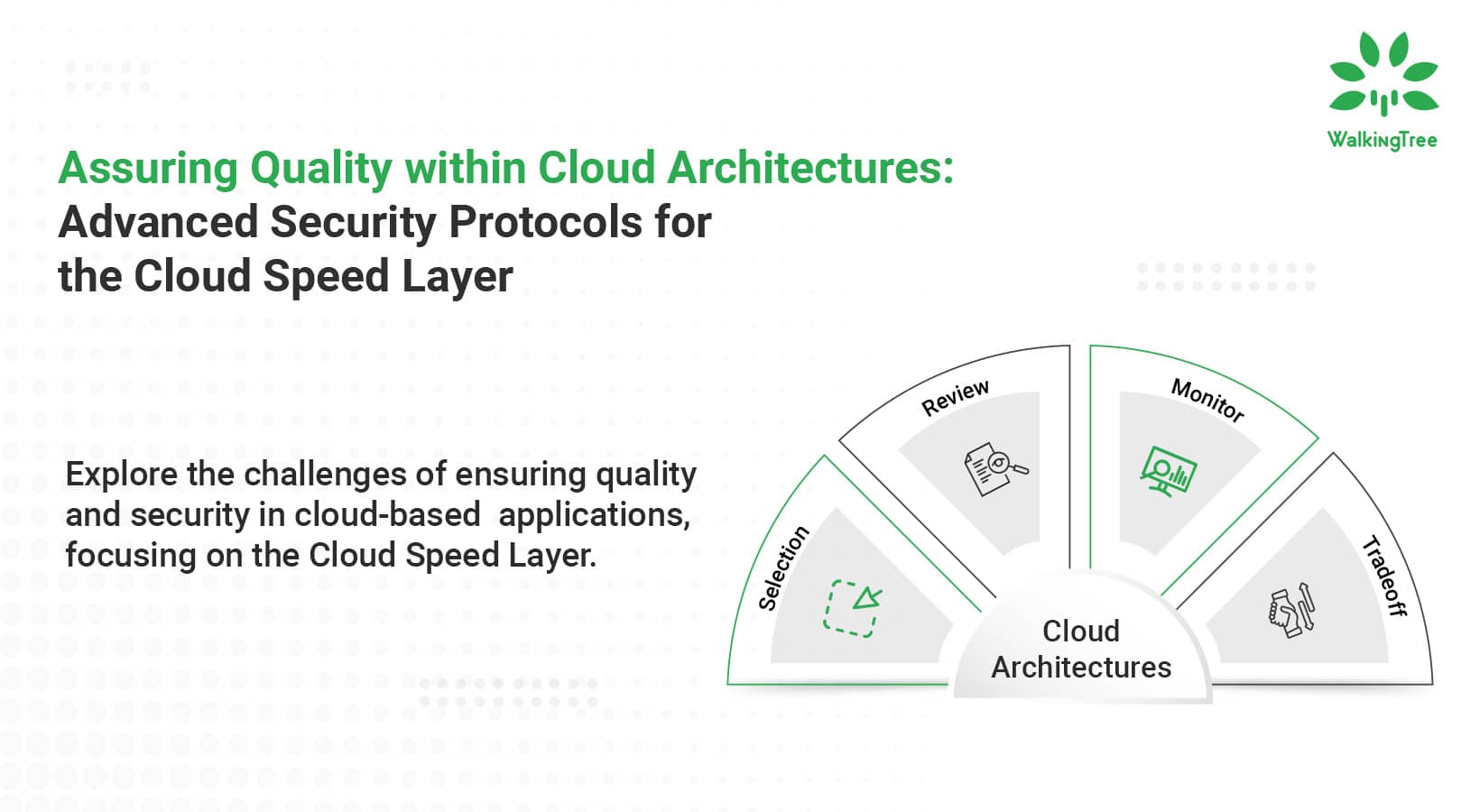
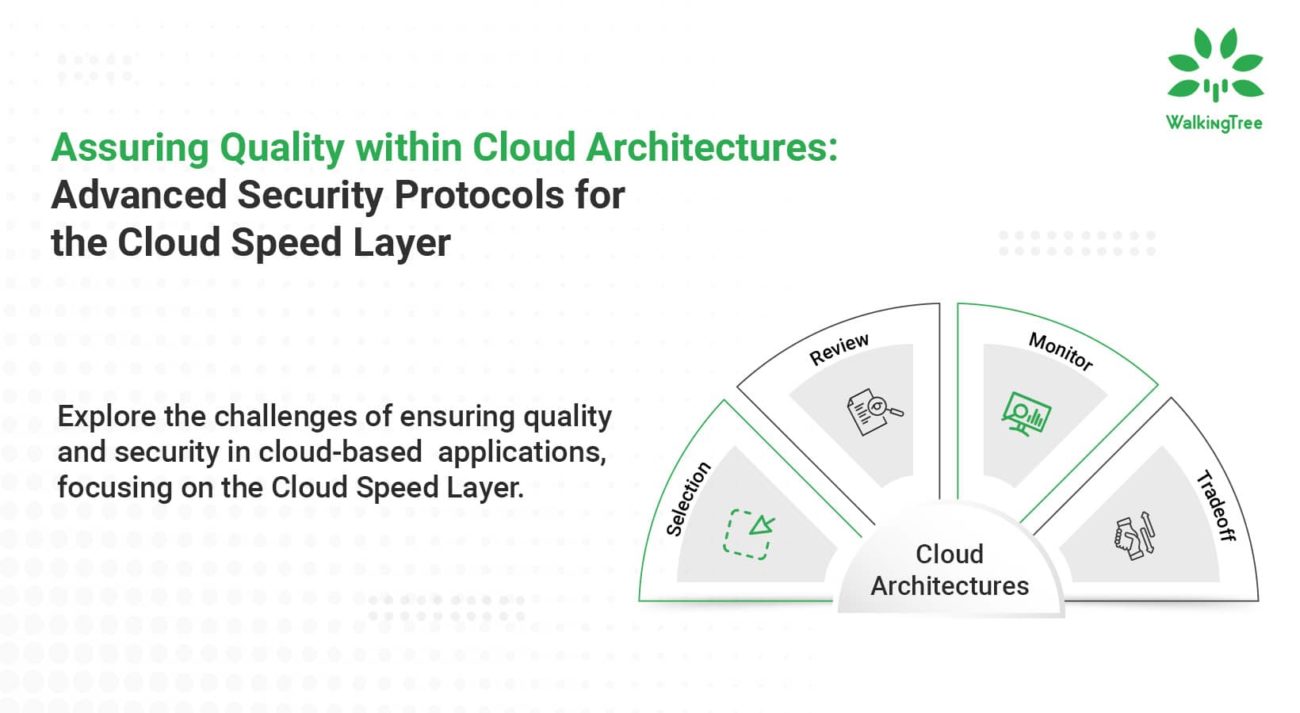
The architecture’s design plays a pivotal role in ensuring operational efficiency and security in cloud computing. Among the various components that constitute cloud architectures, the Cloud Speed Layer, often overlooked, holds significant importance. This layer, dedicated to handling real-time data processing and analytics, faces unique challenges, especially in maintaining stringent security standards. As cloud-based applications become increasingly prevalent, understanding and fortifying the security within the Cloud Speed Layer is not just beneficial; it’s imperative.
|Understanding the cloud speed layer
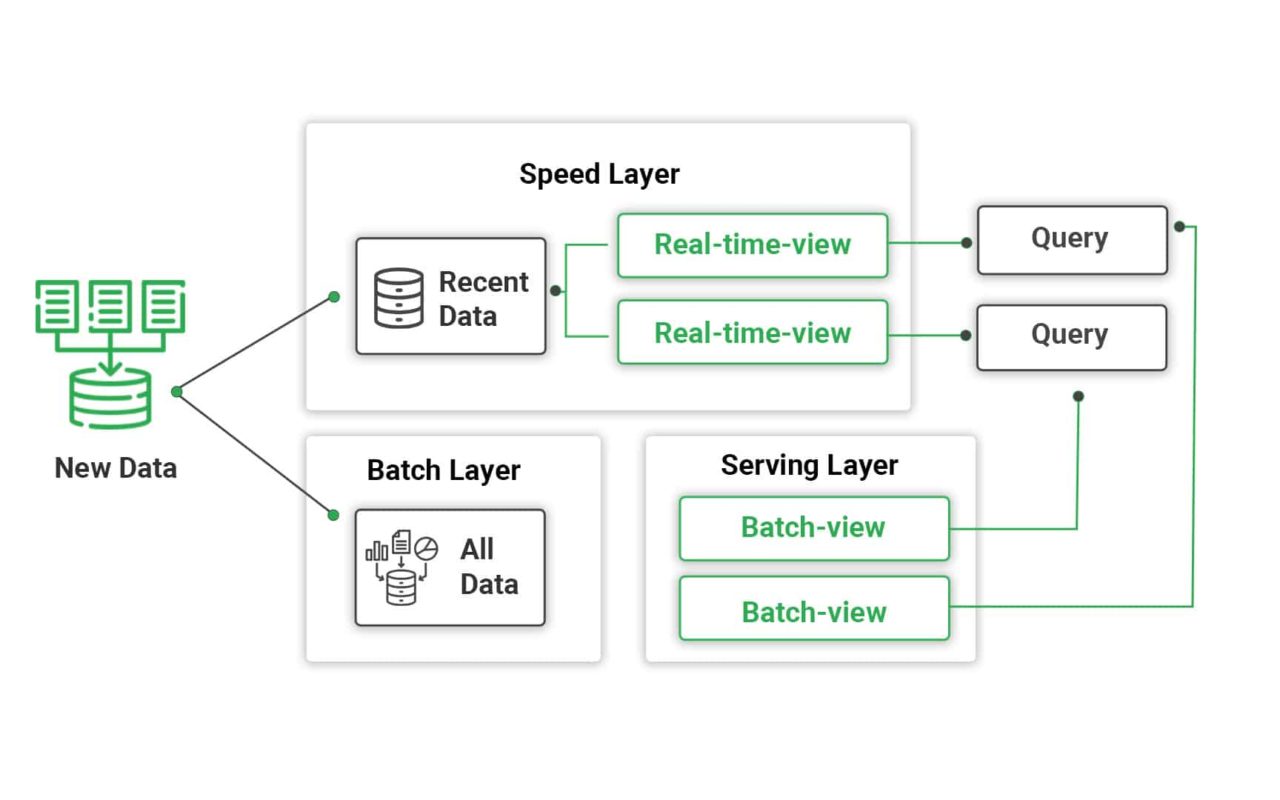
At its core, the Cloud Speed Layer is an essential component of the Lambda and Kappa architectures, designed to manage real-time data processing without the need for batch processing’s latency. This layer’s primary function is to provide immediate insights and responses to dynamic data streams, making it a cornerstone of applications that rely on real-time analytics, such as IoT devices, streaming services, and online transaction systems.
The agility and speed of the Cloud Speed Layer, however, come with their own set of challenges. The real-time processing requirement necessitates that data not only be processed swiftly but also securely, maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of information. Given the layer’s exposure to constantly changing data streams, it becomes a focal point for potential security vulnerabilities.
|Challenges in the Cloud Speed Layer
The Cloud Speed Layer, by its design to process data in real-time, encounters distinct challenges that can significantly impact both the security and the overall quality of cloud-based applications:
- Data Vulnerability: The constant inflow of real-time data makes this layer a prime target for cyber threats. Each data point can potentially be an entry for unauthorized access, making continuous data protection a necessity.
- Scalability vs. Security: As the volume of data increases, the layer must scale accordingly. Balancing scalability with robust security measures is a complex task that requires dynamic solutions.
- Compliance and Privacy: Ensuring compliance with international data protection regulations (such as GDPR and CCPA) in real-time processing environments is challenging. Any lapse can lead to significant legal and reputational damage.
- Latency in Security Protocols: Implementing stringent security checks should not compromise the layer’s primary function—speed. Finding security protocols that offer robust protection without adding significant latency is crucial.
|Advanced security protocols and tools
Addressing the unique challenges of the Cloud Speed Layer requires an array of advanced security protocols and specialized tools:
- Real-Time Data Encryption: Implementing encryption protocols that secure data as it is processed, ensuring that even if data interception occurs, the information remains protected.
- Anomaly Detection Systems: Utilizing AI and machine learning algorithms to continuously monitor data streams for unusual patterns or activities, which could indicate a security breach.
- Microsegmentation: Creating secure, isolated environments within the Cloud Speed Layer can limit the potential damage from any security breach, ensuring that an attack on one segment does not compromise the entire layer.
- Zero Trust Architecture: Adopting a Zero Trust approach ensures strict access controls and verification for every request, minimizing the risk of insider threats.
|Best practices for ensuring quality and security
Beyond the deployment of advanced tools and protocols, adhering to best practices is vital for maintaining the integrity and security of the Cloud Speed Layer:
- Continuous Security Testing: Regular and automated security testing can identify vulnerabilities before they can be exploited, ensuring the Cloud Speed Layer’s defenses remain impervious over time.
- Data Governance Policies: Establishing clear data governance policies helps in managing data effectively, ensuring compliance with regulations, and maintaining data integrity.
- Employee Training and Awareness: Educating employees about the potential security risks and best practices for data handling can significantly reduce the chances of accidental breaches or leaks.
Recent trends in cloud security
 Staying abreast of the latest trends is crucial in a rapidly evolving domain like cloud security:
Staying abreast of the latest trends is crucial in a rapidly evolving domain like cloud security:
- Increased Use of AI and ML for Security: Leveraging AI and machine learning for predictive analytics and real-time threat detection is becoming more prevalent, offering new ways to enhance security measures.
- Rise of Quantum-Resistant Cryptography: With the advent of quantum computing, developing encryption methods that can withstand quantum attacks is gaining traction.
The Cloud Speed Layer is pivotal in modern cloud architecture, demanding an advanced and dynamic approach to security. By understanding the unique challenges, implementing cutting-edge security protocols, and following best practices, organizations can safeguard their cloud environments against evolving threats, ensuring both quality and security in their cloud-based applications.
|Expanding on Advanced Security Protocols and Tools
Real-time data encryption
In the context of the Cloud Speed Layer, real-time data encryption must be both efficient and unobtrusive to avoid adding latency. Advanced encryption standards like AES-256, often used in conjunction with secure key management practices, provide a strong basis for protecting data in transit and at rest. Implementing hardware acceleration for encryption processes can also mitigate performance impacts, ensuring that the speed layer lives up to its name while maintaining high-security standards.
Anomaly detection systems
Modern anomaly detection systems in cloud environments leverage sophisticated machine learning models that are trained on vast datasets to identify patterns and anomalies in real-time data streams. These systems can distinguish between benign anomalies and potential security threats with high accuracy, allowing for immediate automated responses or alerts to security teams. Integrating these systems into the Cloud Speed Layer enhances the ability to detect and respond to threats in real-time, a critical capability given the layer’s exposure to the constant data flow.
Microsegmentation and zero trust
Microsegmentation in cloud environments involves dividing the cloud infrastructure into distinct security segments down to the individual workload level. This approach limits lateral movement within the network, significantly reducing the blast radius in the event of a breach. When combined with a Zero Trust security model—which operates on the principle of “never trust, always verify”—it creates a robust security framework that minimizes the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
|Emphasizing Best Practices
Continuous security testing
Continuous security testing, including penetration testing and vulnerability scanning, should be integrated into the development and deployment pipelines. This practice ensures that new code releases and infrastructure changes do not introduce vulnerabilities. Automated security testing tools can be configured to run these tests at regular intervals, providing ongoing assurance of the security posture without manual intervention.
Data governance and compliance
With cloud architectures, especially those handling real-time data processing, adhering to data governance policies and compliance requirements is paramount. Organizations should establish clear policies for data classification, access control, and data retention. Compliance with frameworks like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA is not just about avoiding penalties but also about building trust with customers and stakeholders by ensuring data confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
|Looking ahead: The future of cloud security
 Cloud security is continuously evolving, with emerging technologies like quantum computing and edge computing presenting new challenges and opportunities. For instance, the development of quantum-resistant cryptography is critical in preparing for a future where traditional encryption methods may no longer be secure against quantum computing attacks. Similarly, as more processing moves to the edge of the network, ensuring the security of edge devices and their connections to the cloud becomes increasingly important.
Cloud security is continuously evolving, with emerging technologies like quantum computing and edge computing presenting new challenges and opportunities. For instance, the development of quantum-resistant cryptography is critical in preparing for a future where traditional encryption methods may no longer be secure against quantum computing attacks. Similarly, as more processing moves to the edge of the network, ensuring the security of edge devices and their connections to the cloud becomes increasingly important.
Assuring quality and security within Cloud Architectures, particularly in the Cloud Speed Layer, requires a multifaceted approach encompassing advanced security protocols, continuous testing, and adherence to best practices. As cloud technologies continue to evolve, so too will the strategies and tools needed to protect them. By staying informed of the latest trends and threats and adopting a proactive, layered security stance, organizations can safeguard their cloud environments against the ever-changing landscape of cyber threats.
Click https://analytics.walkingtree.tech/cloud-native/ to gain exclusive access to expert insights on real-time data encryption, anomaly detection systems, micro-segmentation, and more.