Blogs
Conquering the 3Vs of Data Management: Volume, Variety, and Velocity
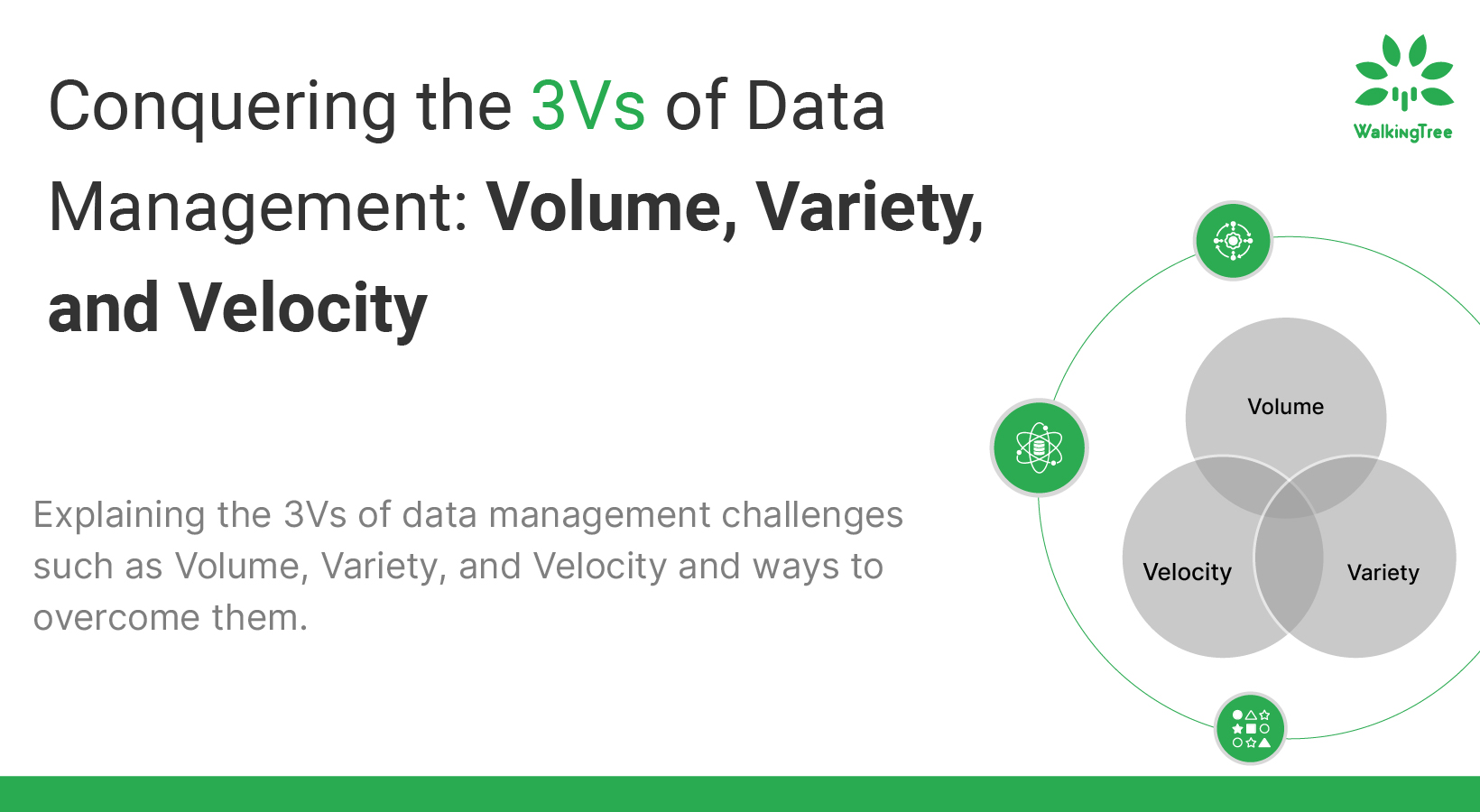

Data is the vital component that drives businesses ahead, sparks creativity, and guides tactical choices. However, maximizing this enormous resource could be difficult, especially when balancing the “3Vs” of data management: volume, variety, and velocity. Based on my deep experience as a data architect, I can say that I have seen businesses struggle with these nuances. However, I have also seen the effective tactics that can be used to both handle and benefit from these difficulties.
The Challenge: Data Volume, Variety, and Velocity
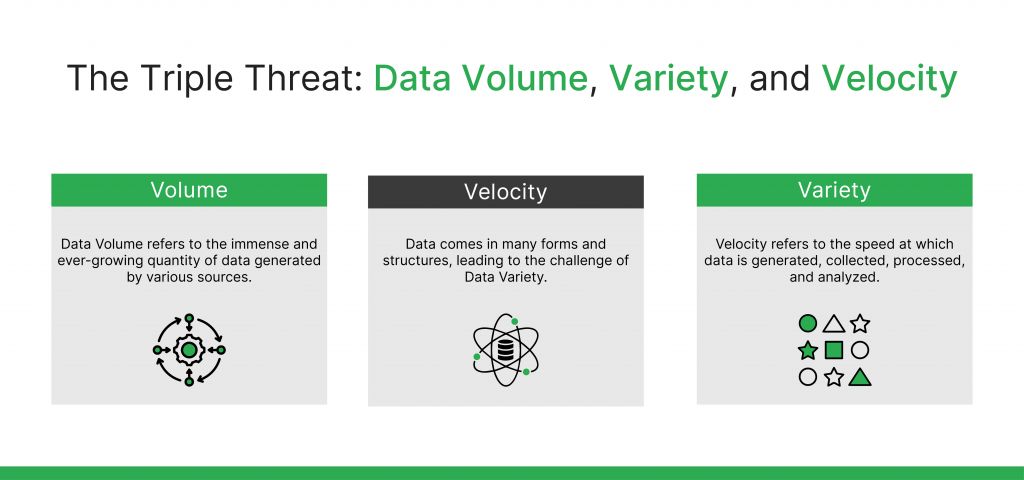
Data Volume refers to the sheer amount of data generated every second. From social media posts to IoT sensor readings, businesses are inundated with data. Variety refers to the different types of data – structured, unstructured, and semi-structured – that organizations must handle. Velocity refers to the speed at which data is created, processed, and analyzed.
Data Volume
The massive and continuously growing amount of data that is provided from many sources is known as data volume. This encompasses a vast array of data, including real-time data streams from social media, Internet of Things devices, and online transactions in addition to conventional databases.
In this case, the challenge is not only how much storage is required, but also how to effectively access, process, and analyze so much data to draw actionable conclusions. More data means more complexity and expense in data management.
Organizations must use contemporary data storage solutions like cloud storage and data lakes along with scalable processing technologies like distributed computing to effectively handle this challenge.
Data Variety
Data comes in many forms and structures, leading to the challenge of Data Variety. This variety includes:
Structured Data: Highly organized and easily searchable data, typically stored in relational databases. Examples include Excel files or SQL databases with clear rows and columns.
Unstructured Data: Due to its lack of a preset format or organization, unstructured data is more challenging to handle and analyze. This includes written content in addition to images, videos, and social media updates.
Semi-structured Data: A blend of structured and unstructured data elements. Examples include JSON and XML files, where the data is tagged or marked up but doesn’t fit into the rigid structure of a database.
To handle this diversity, methods for sophisticated and adaptable data modeling and processing are required. Organizations must employ standard databases for structured data and modern data processing frameworks and machine learning approaches for unstructured and semi-structured data.
Data Velocity
Velocity is the pace at which information is generated, obtained, handled, and examined. An unprecedented amount of data has been generated as a result of real-time analytics, the Internet of Things, and streaming services. This data needs to be used quickly to maintain its value. Rapid data aging is implied by high velocity, which emphasizes the importance of prompt processing and analysis.
Organizations need to use real-time analytics and data processing technology to solve velocity. This includes fast data consumption, processing, and analysis frameworks for stream processing, event-driven architectures, and in-memory databases. The speed at which unprocessed data may be turned into insightful knowledge can boost decision-making significantly and provide an edge over rivals.
|Solutions for the Volume, Variety, and Velocity Challenges

To address the problems posed by the digital landscape, a comprehensive approach to data management and analytics is necessary, considering the volume, diversity, and velocity of data. To solve these issues and make the most of their data assets, organizations need to use a variety of innovative technologies, tactics, and skills.
Enhanced Data Governance
To keep data safe, accurate, and high-quality, data governance is essential. To guarantee legal compliance and protect sensitive data, comprehensive rules and procedures for data access, usage, and management must be developed. Organizations may ensure the appropriate and efficient use of their data assets by putting strong data governance frameworks in place and maintaining control over their data assets.
Strategic Data Integration
The integration of disparate data sources becomes essential for a cohesive view as data becomes more abundant and diversified. Data integration platforms and technologies simplify the process of combining data from various sources, boosting consistency and accessibility. As the foundation for comprehensive analytics, this unified data repository offers deeper insights and facilitates informed decision-making throughout the whole enterprise.
Leveraging Advanced Analytics and AI
Transcending conventional analytical capacities is made possible in large part by AI and advanced analytics. Deeper insights, trend forecasts, and strategic decision-making can be achieved through the use of machine learning, predictive analytics, and AI-driven technologies. By utilizing these technologies, firms may fully utilize their data and convert it from unprocessed information to insightful knowledge that can be put to use.
Cultivating a Skilled Workforce
Modern data administration is complex, requiring a team with the right skills who are knowledgeable about the newest data technologies and methods. The team will be able to handle the changing problems of Volume, Variety, and Velocity if they continue to invest in training and development. This will keep them at the forefront of data management technologies.
Fostering a Data-Driven Culture
Effective data utilization requires the organization to instill a data-driven culture. This entails boosting data literacy at all levels, supporting decision-making based on data, and appreciating data’s usefulness as a tactical asset. Teams are empowered, collaboration is improved, and the organization is aligned toward shared data-centric objectives when there is a data-driven culture.
|Real-life Scenario & Respective Solutions
Consider a multinational e-commerce business that we’ll refer to as an “E-Shop”. Millions of people use E-Shop worldwide, and with each click, purchase, and review, a customer generates data. This data is available in three different formats: semi-structured (like customer emails), unstructured (like customer reviews), and structured (like transaction information). Moreover, this data is created in real-time, necessitating fast processing to deliver personalized suggestions, detect fraudulent transactions, and check inventory.
E-Shop’s traditional databases were becoming overloaded with data, causing delayed query replies and system breakdowns. Because of the diversity of the data, important insights from semi-structured and unstructured data were frequently missed. Due to the rapid rate of data collection, E-Shop found it difficult to offer fraud detection and real-time customisation.
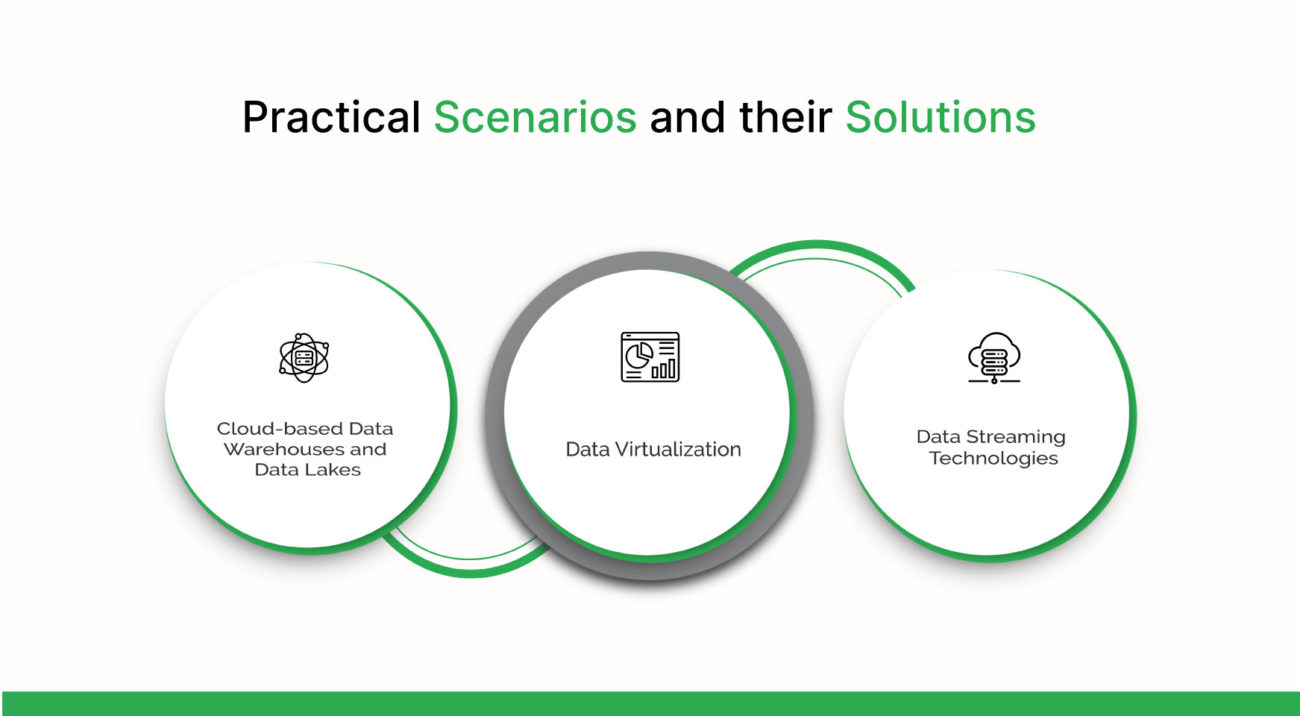
To tackle these challenges, E-Shop implemented a three-pronged strategy:
- Cloud-based Data Warehouses and Data Lakes: To handle the volume of data, E-Shop moved its data storage to the cloud. Cloud-based data warehouses and data lakes provided the necessary scalability and flexibility, allowing E-Shop to store and process petabytes of data without overwhelming its systems.
- Data Virtualization: To address data variety, E-Shop adopted data virtualization techniques. This allowed E-Shop to access and analyze different types of data from a single point, regardless of the data’s format or physical location.
- Data Streaming Technologies: To manage data velocity, E-Shop implemented data streaming technologies. These technologies allowed E-Shop to process and analyze data in real time, enabling immediate personalization, fraud detection, and inventory monitoring.
|Conclusion
Businesses face enormous hurdles when it comes to the 3Vs of data: volume, variety, and velocity. However, these difficulties can be successfully handled if the appropriate tactics and tools are used. In the instance of E-Shop, embracing data virtualization, cloud-based storage, and data streaming technologies turned obstacles into possibilities, revealing insightful information and promoting company expansion.
WalkingTree Technologies helps businesses maximize their data management strategies by transforming data issues into valuable insights. WalkingTree Technologies is highly adept at handling the three Vs of data: volume, variety, and velocity. Modern technologies including cloud-based storage, real-time analytics, and data virtualization are utilized by the organization. Data-centric decision-making is aided by several services, including advanced analytics, integration, migration, and data engineering. Further strengthening data-driven cultures are predictive analytics, data governance, and AI/ML applications. The company’s expertise includes creating scalable data ecosystems, implementing end-to-end digital transformation solutions, access management, real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and conversational AI.
So, if your organization is grappling with the 3 Vs of data, remember E-Shop’s story. The right solution can turn your data deluge into a goldmine of insights.